Motion detection technology has emerged as a cornerstone in modern security systems, offering unparalleled capabilities in detecting and responding to potential threats. From its humble beginnings to the sophisticated algorithms of today, motion detection has revolutionized Security, providing enhanced monitoring and protection across various environments. This article delves into the introduction of motion detection in security cameras, exploring its evolution, principles, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Evolution of Motion Detection

The evolution of motion detection in security cameras traces back to rudimentary sensor-based systems, gradually evolving into complex algorithms powered by artificial intelligence. Early iterations relied on basic infrared sensors or pixel-based motion detection algorithms. However, with advancements in computer vision and machine learning, modern motion detection systems employ intricate mathematical models and pattern recognition techniques to discern relevant motion from background noise.
Key Principles

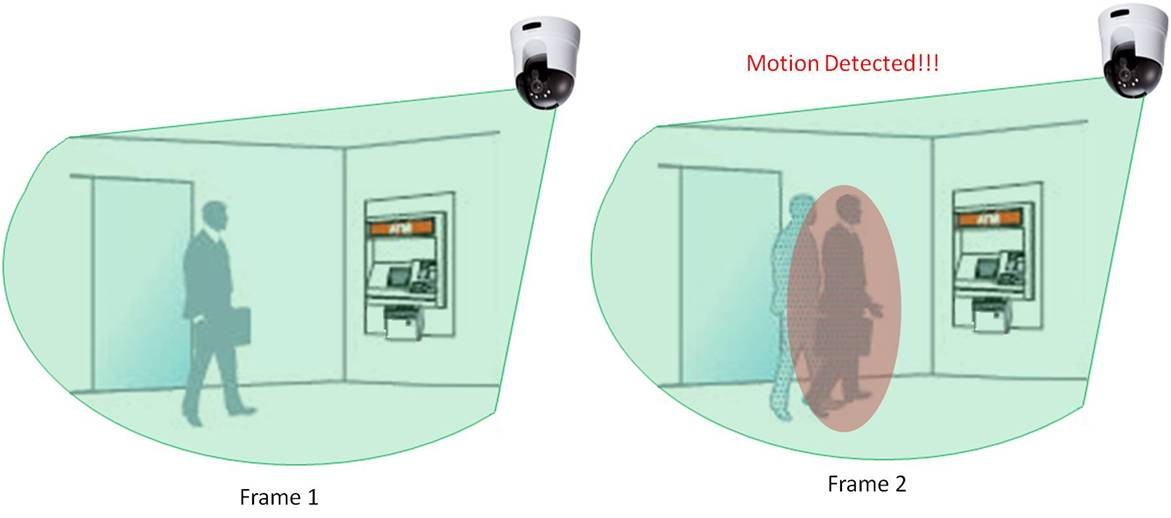
At its core, motion detection involves analyzing changes within the camera's field of view. This encompasses detecting alterations in pixel values, object movement, or variations in infrared radiation. The principles underpinning motion detection algorithms include thresholding, background subtraction, and motion tracking. By employing these techniques, security cameras can accurately identify and respond to potential threats in real-time.
Applications

Motion detection technology finds widespread applications in various security scenarios, including:
Security Systems: Deployed in homes, businesses, and public spaces to detect unauthorized intrusions or suspicious activities.
Smart Home Security: Integrated into smart home systems for remote monitoring and alerts.
Retail Analytics: Used by retailers to track customer behavior and prevent theft.
Traffic Management: Employed in traffic monitoring systems to optimize traffic flow and detect accidents.
Industrial Security: Ensures the safety and security of industrial facilities by identifying potential hazards and unauthorized access.
Benefits

The integration of motion detection in security cameras offers several benefits, including:
Efficiency: By triggering recording or alerts only when motion is detected, motion detection reduces the need for continuous monitoring, conserving resources.
Enhanced Security: Prompt alerts enable timely responses to potential threats, deterring criminal activity and minimizing risks.
Cost-Effectiveness: Motion detection technology reduces operational costs associated with manual Security efforts.
Customization: Users can customize sensitivity settings and define specific detection zones, enhancing adaptability to diverse environments.
Challenges and Considerations

Despite its advantages, motion detection technology faces challenges and ethical considerations, including:
False Alarms: Inaccurate detection may lead to false alarms, causing disruptions and reducing system reliability.
Privacy Concerns: The widespread deployment of Security cameras raises privacy concerns regarding data collection and potential misuse.
Algorithm Bias: Biases in motion detection algorithms may result in discriminatory outcomes or false assumptions, necessitating ongoing evaluation and refinement.
Future Trends

The future of motion detection in security cameras is characterized by advancements in AI, deep learning, and edge computing. This includes the development of more sophisticated algorithms capable of recognizing complex activities and behaviors, as well as enhancing privacy protections through anonymization and transparency measures.
Motion detection technology represents a pivotal advancement in security Security, offering unparalleled capabilities in threat detection and response. Despite facing challenges such as false alarms and privacy concerns, ongoing advancements in technology and ethical considerations will continue to shape the evolution of motion detection, ensuring both effectiveness and accountability in security practices.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.